2. EXISTING REPRESENTATIONS ABOUT ALLOCATION AND QUASARS NATURE
|
|
2. EXISTING REPRESENTATIONS ABOUT ALLOCATION AND QUASARS NATURE |
 |
Investigations of the Universe through radio telescopes have resulted in discovery such surprising objects as quasars. The increased resolving ability of radio telescopes has served as the background of quasars discovery. It has allowed defining the coordinates and angular sizes of objects emitting radio waves with more accuracy than earlier.
Quasars discovery
Two 27-meter antennas of the California technology institute which locate in Owens valley represented in pair with each other the radio interferometer have begun coordinates measurement of the radio emission sources which have been recorded in the 3rd Cambridge catalogue (3C) in 1960. The accuracy of coordinate determination has reached ![]() and as result measurements was discovered that some sources have the very small angular sizes.
and as result measurements was discovered that some sources have the very small angular sizes.
September 26, 1960. T. Met'juz and A. Sandage have photographed on a 200-inch telescope of the sky area containing one of such sources 3C 48. Within a rectangle of coordinates errors in this area there were no objects except for the star ![]() . Around the star there were tracks of feeble nebula but the object looked star-shaped. October 22, 1960. A. Sandage has investigated a spectrum of the discovered object, in which there was a strong combination of broad emission lines, which was impossible to identificate. Any of spectral lines was not possible to know in its spectrum, lines was not possible to identify no with one chemical element. The color indexes 3C 48 were unusual too, they corresponded to very hot objects with ultra-violet excess.
. Around the star there were tracks of feeble nebula but the object looked star-shaped. October 22, 1960. A. Sandage has investigated a spectrum of the discovered object, in which there was a strong combination of broad emission lines, which was impossible to identificate. Any of spectral lines was not possible to know in its spectrum, lines was not possible to identify no with one chemical element. The color indexes 3C 48 were unusual too, they corresponded to very hot objects with ultra-violet excess.
By 1962 T. Met'juz and A. Sandage have identified with star-shaped objects the radio emission sources 3C 196 and 3C 286. 1963 became decisive, to this time of K. Hazard, M. Makkej and A. SHimins with record accuracy determined the coordinates of radio emission source 3C 273. The object has appeared double with distance between components in ![]() and diameter of each source less
and diameter of each source less ![]() . One of source components coincided with "feeble star" (
. One of source components coincided with "feeble star" (![]() ). Young Dutch astrophysicist Maarten Schmidt on observatory Mt. Palomar has investigated the spectrum 3C 273, in which again there were incomprehensible emission lines. Just he has supposed that these lines can be identified with the Balmer hydrogen line if to admit red shift equal 0,158.
). Young Dutch astrophysicist Maarten Schmidt on observatory Mt. Palomar has investigated the spectrum 3C 273, in which again there were incomprehensible emission lines. Just he has supposed that these lines can be identified with the Balmer hydrogen line if to admit red shift equal 0,158.
The correctness of line identification offered by Schmidt was proved by Dj. Ouk, which has found in the infrared spectrum 3C 273 line ![]() in accuracy on that place where it should be with offered value of red shift. After the specified event T. Met'juz and Dj. Grinstejn identified lines in the spectrum 3C 48 having supposed red shift
in accuracy on that place where it should be with offered value of red shift. After the specified event T. Met'juz and Dj. Grinstejn identified lines in the spectrum 3C 48 having supposed red shift ![]() .
.
Nine such objects became known to the end of year and then the flow of discovery has gushed when became clear on what attributes is possible them to search. By 1967 was already found about 150 quasi-sidereal radio emission sources (quasistellar sourse, QSS), in 1977 them became 370 and very soon the name quasar (for such objects) was coined.
Basic observed properties of quasars
The quasars at observation through a telescope look like as star-shaped objects, which besides are strong sources of radio emission. They have excess of radiation in ultra-violet and infrared area of a spectrum. Spectrum contains broad lines of radiation, always strongly shifted in the red side.
The quasars have a number of surprising properties:
a) The power of their electromagnetic radiation is extremely great from ![]() up to
up to ![]() W. For comparison we shall specify that the power of radiation of our Galaxy amount approximately
W. For comparison we shall specify that the power of radiation of our Galaxy amount approximately ![]() W. It is supposed, that this high-power radiation can arise at a gravitational collapse of huge weight from
W. It is supposed, that this high-power radiation can arise at a gravitational collapse of huge weight from ![]() up to
up to ![]() Solar weight;
Solar weight;
b) The spectrum of radiated light finds out strong red shift characterized in parameter ![]() , where
, where ![]() - wavelength of observation light, and
- wavelength of observation light, and ![]() - its red shift in the side of long waves. This red shift is so great that, for example, the line
- its red shift in the side of long waves. This red shift is so great that, for example, the line ![]() of series Lyman in a hydrogen spectrum, at standard conditions observed in ultra-violet area, appears in a visible part of a spectrum;
of series Lyman in a hydrogen spectrum, at standard conditions observed in ultra-violet area, appears in a visible part of a spectrum;
c) The quasars change their brilliance, at some the oscillation frequency of brilliance reaches up to ![]() and more. For example, the quasar 3C 279 has the amplitude amount almost
and more. For example, the quasar 3C 279 has the amplitude amount almost ![]() and in a maximum of brilliance it is one of the brightest objects of the Universe, its
and in a maximum of brilliance it is one of the brightest objects of the Universe, its ![]() ;
;
d) Feeble nebula ambient quasars were discovered, radiation of nebula so feeble, that for their ephemeral view the English and American astronomers named them beautifully as "fuzz". So, in the center of such "fuzz" which is the size of a giant galaxy, a quasar like dense, tiny corn of a poplar in its shell is located.
The energy-release of quasars is huge. The luminosity of our Galaxy as was already mentioned amounts to about ![]() W; the quasar luminosity on some orders is higher. Total energy emitted by quasars is estimated in
W; the quasar luminosity on some orders is higher. Total energy emitted by quasars is estimated in ![]() watt-second. It is in 10 billions times more than the Sun has emitted for all time of its existence.
watt-second. It is in 10 billions times more than the Sun has emitted for all time of its existence.
Variability of quasars radiation is found out both in optical and in a radio-frequency range. The oscillations of luminosity occur in times by an irregular mode about one year and less (up to several days). Therefore, it is possible to make a conclusion, that the sizes of quasars do not exceed a route transited by light during essential change of luminosity otherwise variability would not be observed. Hence, it is indirectly possible to estimate the sizes of quasars, their diameters do not exceed one light year, i.e. the quasars are smaller even of single galaxies (For comparison the diameter of our Galaxy about 100 thousand light years). From here follows that all the huge energy of a quasar is generated in an insignificant small volume.
Starting from such observed quasars properties several guesses were made:
Either
1) Or these objects located very much far outside a Galaxy and luminosity of objects in 100 and more time exceeds a luminosity of giant galaxy,
2) Or the quasars are objects thrown out from a kern of a Galaxy with tracks of explosive activity of kerns and moving with huge velocity, then distance up to them can be estimated by value about 106-107 parsecs, hence, and these objects radiate much less energy.
In the beginning the observed red shift tried to explain at the expense of Doppler effect. Then the quasars should flee from us with huge velocity. Quite often therefore it is possible to meet in the literature the identification of the parameter ![]() with the relativistic Doppler shift
with the relativistic Doppler shift ![]() , which comes on change to nonrelativistic Doppler shift
, which comes on change to nonrelativistic Doppler shift ![]() , when the relative velocity
, when the relative velocity ![]() becomes close to velocity of light in vacuum
becomes close to velocity of light in vacuum ![]() . Thus, the quasars should flee from us with velocity, close to velocity of light in vacuum. Such explanation, however, looks rather doubtful. Besides, the guess suggested in this connection that the quasars represent objects thrown out by kerns of galaxies of a Local galactic congestion with almost velocity of light removed from us no more than on 10 millions a parsec (1 parsec = 3,26 light years =
. Thus, the quasars should flee from us with velocity, close to velocity of light in vacuum. Such explanation, however, looks rather doubtful. Besides, the guess suggested in this connection that the quasars represent objects thrown out by kerns of galaxies of a Local galactic congestion with almost velocity of light removed from us no more than on 10 millions a parsec (1 parsec = 3,26 light years = ![]() m), puts many new problems.
m), puts many new problems.
Today almost everyone recognizes that the shift of quasar spectra in the side of long waves is explained not by Doppler effect, and it generates the cosmological red shift. According to this explanation, the further from us is located a quasar, the more its spectrum is shifted in full conformity with cosmological effect of Hubble.
Cosmological models of the Universe
Any hypotheses and guesses explaining observed properties of the Universe always are formulated on the basis of definite cosmological model. Now in a cosmology there are two main models. The first model is based on a General Relativity (GR) and named as the model of observed Einstein-Fridman Universe. The second model was offered by such scientists as Bondy, T. Gold, F. Hoil and named as the model of the stationary Universe.
In both models is recognized that the large-scale structure of the Universe is identical everywhere and in all directions, i.e. the Universe is homogeneous and isotropic. But "the Perfect cosmological principle" the theory of the stationary Universe says that, besides that the Universe is identical not only everywhere, but also always. In the theory of observed Einstein-Fridman Universe there are solutions of two types. According to first, the Universe is dynamic and is continuously dilating after a so-called The Big Bang (the moment of the Universe birth). In the second version the expansion slows down more and more, and then will be replaced by squeeze and the Universe will be squeezed to a condition of extreme large density (condition of a singularity), and then again expansion will begin.
Today, the cosmological model of Einstein-Fridman is traditional and universally recognized and all explanations of observed properties of the Universe are created, as a rule, on the basis of the specified model.
Hypotheses about a quasars nature within the framework of conventional cosmological model
Quasars as defined stage of the Universe development
The statistical analysis of quasar red shift has shown that the values ![]() in general do not exceed defined value
in general do not exceed defined value ![]() and shows the tendency to concentrate in an interval from
and shows the tendency to concentrate in an interval from ![]() up to
up to ![]() . In the beginning this is explained that because of absorption of light in interstellar gas the farther objects are inaccessible to modern telescopes. However, later the other explanation was put forward.
. In the beginning this is explained that because of absorption of light in interstellar gas the farther objects are inaccessible to modern telescopes. However, later the other explanation was put forward.
According to it even with the help of more perfect telescopes dilating horizons by the observed Universe which allow to glance in its farther past, it is impossible to discover new more remote quasars since before the defined moment they simply did not exist. And this moment already now is within the reach of our telescopes. According to this cosmological interpretation since the radiation received by us from quasars today goes up to us about 10 billions years then the researchers observing the quasars is looking in the past of the Universe on 10 billions years back. The Universe then was at earlier stage of development and the processes taking place in its, differed by huge energies. It also explains unusual power of quasar radiation.
Starting from such guess, it is possible to consider, that the quasars correspond to a defined phase of development of the Universe as a whole, and are a characteristic feature for its, far past. Accordingly, up to quasars existing on early phases of the Universe development there should be huge distances, which the observations confirm.
Confluence of galaxies as the reason of a quasars phenomenon
Observations and researches of the "fuzz" images around quasars have resulted in new discovery. It is discovered that many of the "quasars" galaxies interact with other galaxy. Percent of such pairs is rather high and it reaches 30 % in the systems with small red shift. Such facts observed allow to suppose that phenomenon of a quasar in many cases can be aroused by the galaxies interaction.
The specified hypotheses are that the interaction of galaxies strongly perturbs motion of gas in a system, and it falls to the center of a galaxy. There, a supermassive black hole "gobble up" it and this process is accompanied by liberation of huge quantity of energy, which we observe as a phenomenon of a quasar.
The modern researches show that the processes of confluence galaxies and the processes of activity of galactic kerns correlate among themselves. In this connection it is possible to suppose, that the epoch of quasars formation can be simultaneously by epoch of formation of massive galaxies at the expense of merging less massive units (dwarf galaxies). Straight observations of master's galaxies (galaxies, which swallow up other galaxy) the nearest quasars through the Hubble telescope have given confirmation of straight connection the activity with interaction and confluence of galaxies. In particular, in case of master's galaxy of quasar PKS 2349 is discovered that the satellite galaxy of a scale BMO is immersed in its.
According to the above-stated the quasars represent a rather complicated accretion system around a supermassive black hole located in the center of a master's galaxy. It is so-called accretion disk and a shaded disk or thick disk on which axis the radiolet is directed in case of radioloud objects, the system of fast flying clouds, which shape broad optical emission lines, and on large distances behind a disk give narrow optical emission lines.
Similar "assembly" of galaxies is observed with the help of the Hubble telescope on red shift about 2-3. Such process can explain both as fast decrease of number of quasars from the past to the present and well-known rupture in their distribution on large red shift. The radioloud quasars in model of confluence communicate with the rotation of a black hole, which is initiated or recent "strong" confluence of a comparable weight galaxies or rather small quantity of "feeble" confluence of a massive galaxy with dwarfs. Besides it is considered, that the confluence lead to occurrence of activity of galactic kerns.
Quasars as a defined phase of a galaxy life
Many characteristics of quasars are observed and at galaxies, i.e. between quasars and galaxies there is a continuous connection. Such galaxies reveal in the spectrum strong ultra-violet excess, some have appreciable red shift and are not sources of radio emission. The brightness of galaxies are much less than quasars. The radio emission was also found in some galaxies they were named by N-galaxies.
The spectra of quasars are similar to spectra of kerns Seyfert galaxies that in the field of the kern have broad emission lines indicating on the motion of large mass of gas. The energy distribution in a spectrum is also similar. The characteristics both radio emission and polarization of quasars light and galaxies differ from each other a little. The high-power flows of infrared radiation are observed both from quasars and from kerns Seyfert and radio galaxies. Therefore, hypotheses were put forward that the quasars are active and superpower kerns of remote, young galaxies.
Especially important and convincing evidence of nature unity of quasars and galaxies was the detection in 1967 by Dj. Ouk of brilliance variability of a unobstructive radio galaxy 3C 371 with amplitude about ![]() . The brilliance variability of several N-galaxies and Seyfert galaxies soon also were discovered. It turned out, that the brilliance variability is not a unique property of quasars, and this property is peculiar to galaxies with an active kern.
. The brilliance variability of several N-galaxies and Seyfert galaxies soon also were discovered. It turned out, that the brilliance variability is not a unique property of quasars, and this property is peculiar to galaxies with an active kern.
The likeness of quasar properties with properties of kerns Seyfert galaxies has given the basis to assume that the quasars are kerns of young galaxies.
More late observations in the beginning of 70's and in 80's years of XX century have shown that the discovered feeble nebulas around quasars in color are similar to late blue spiral galaxies and sometimes are even bluer. The blue color of galaxy indicates upon plenty of young massive stars. It can mean that a nebula represents a young galaxy in which there is a high-power process of star formation.
In 1982 the American astronomers T. Boroson, Dj. Ouk, K. Grinss could found a good spectrum of nebula around quasar 3C 48 and have found in it, a narrow, typically stellar line of magnesium absorption. It was the first direct proof that the quasars are surrounded by stellar component and they are possibly considered as kerns of born galaxies.
Conventional representations about quasars distribution in space
Detection chronology of new quasars, a ways of their search
Since the moment of discovery the quantity of the detected quasars is constantly increased. In process of perfection of technical and methodological means of search and identification it is discovered more and more far quasars. But if to analyse the detection chronology of these objects then the next feature of quasars comes to light.
From the moment of quasars discovery in 1963 the process of detection of new quasars went very fast, but after achievement by red shift of value ![]() dynamics of this process was considerably slowed.
dynamics of this process was considerably slowed.
If to analyse technical ways of quasars detection, it is possible to see, that at first mainly the radioloud quasars are discovered then since 1965 radiosilent quasars are discovered. They are discovered as blue objects, using the test of "ultra-violet excess". But such technique of quasar detection becomes inefficient at values of red shift exceeding 2 and this fact could explain slowing down the rates of discovery of new quasars.
At the end of 80's of XX century new more effective optical techniques of quasar detection have appeared. It has allowed in the first time, to discover quasars with large value of red shift. But, despite of large-scale researches with application of modern tests of detection and identification it was very difficult to find quasars with red shift exceeding 5,5. The question emerges whether it is possible to discover quasars with large value of red shift. Despite of limitations in modern methods of detection the quasars in general should be discovered at values ![]() . Such situation has resulted in the guess that on farther distances the quasars practically do not meet. And density of a spatial distribution of quasars is fast incremented in range of values
. Such situation has resulted in the guess that on farther distances the quasars practically do not meet. And density of a spatial distribution of quasars is fast incremented in range of values ![]() , and then is sharply reduced for large values of red shift (see Fig. 1).
, and then is sharply reduced for large values of red shift (see Fig. 1).
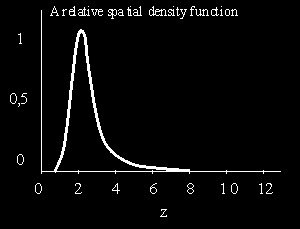
Fig. 1. A relative spatial density function of quasars
Periodicities in quasars spectra
The researches of quasars were carried out not only through telescopes. The considerable interest for researches was represented the fixed coordinates of already discovered quasars. The statistical researches of quasar distribution in space in increase process of quantity of discovered quasars gave the more and more interesting results.
The researches of quasar distribution were carried out on different parameters including on value of red shift ![]() . Thus in general, histograms of distribution are built, explored peaks in quasar distribution especially nearby
. Thus in general, histograms of distribution are built, explored peaks in quasar distribution especially nearby ![]() , but the further statistical analysis, as a rule, was not carried out.
, but the further statistical analysis, as a rule, was not carried out.
The correlation analysis of a histogram of quasar distribution was carried out in 1971 by Carlsonn, who has revealed qualitatively new feature of distribution of quasars in space, the periodicity of distribution on argument ![]() . Calculation of an auto correlation function has confirmed presence of the specified periodicity. The sample of 166 objects was explored, and the period
. Calculation of an auto correlation function has confirmed presence of the specified periodicity. The sample of 166 objects was explored, and the period ![]() on argument
on argument ![]() has made 0,205.
has made 0,205.
Such fact, in a spatial distribution of quasars on red shift required an explanation, and originally reason of occurrence such irregularity was seen in techniques of quasars detection (effects of selection). But in the further the conclusion about strong influence of effects of selection was doubted and the objections against non-uniformity in distribution of quasars on ![]() were rejected.
were rejected.
The statistical researches of coordinates of discovered quasars were continued, the more and more new samples, for a lot of objects were under construction, but the result remained the same, the red shift of discovered quasars tended to avoid some intervals ![]() .
.
Today, the researches of periodicity in a spatial distribution of quasars are continued, but precise physical interpretations within the framework of conventional cosmological model of the Universe have not obtained.
Conclusion
Any facts observed should be liable to careful understanding and what obvious was this or that fact always there should be a defined shadow of doubt in the validity of interpretation of this fact.
As it was possible to see, within the framework of the traditional and universally recognized cosmological model of the Universe there are enough of difficulties and contradictions at interpretation of discovered properties of the actual world. Therefore to accept peremptory this model is still early. Hence, it is in our common interests that to listen to the non-traditional points of view on apparently already solved problems.
You know that the only model of the actual world can apply for the validity in which there will not be any contradictions and misfit with all observation facts of the actual world in a complex. Because "the variety of ways lead to a mistake and the only one leads to the truth".