6. ESTIMATION OF LOCAL INHOMOGENEITIES IN QUASARS ALLOCATION
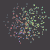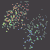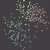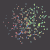
|
|
6. ESTIMATION OF LOCAL INHOMOGENEITIES IN QUASARS ALLOCATION |
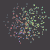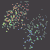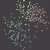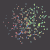 |
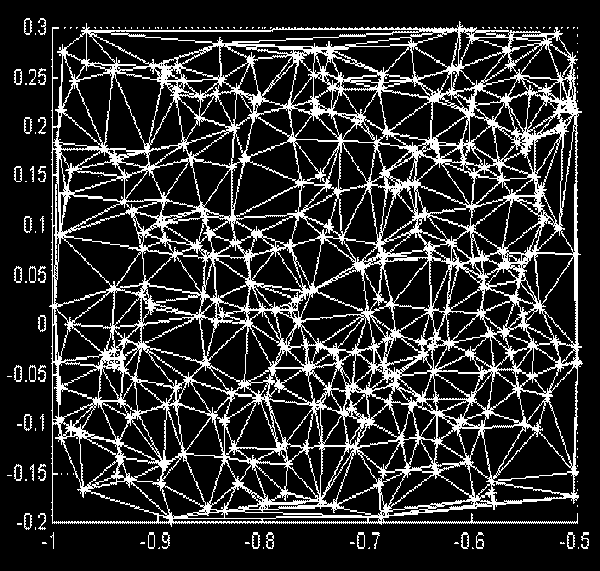
The Delone triangulation is a set of lines pairing each quasar with its nearest neighbouring quasars. These lines not intersect and to form the delta circuits. From here the name of the triangulation method was formed.
The Delone triangulation allows to determine all distances between quasars in thin area of the Universe (i.e. practically on a plane). Further the statistical handling of multitude of these distances is carried out that allows to obtain objective appraisal of large-scale allocation of quasars in the Universe, and also to determine structure of the Universe as a whole. After that the initial model of the Universe is confirmed or rejected.
We shall show for example how the Delone triangulation method for area 1 was used. We shall remind that about 380 quasars are in this area. Thus about 750 distances between quasars is formed provided that the lines between quasars are not intercrossed (see Fig. 1).
Further we have constructed a histogram (Fig. 2). Here density of quasars ![]() is put aside on a vertical axis. Distance between the nearest quasars is put aside on a horizontal axis. The histogram shows that the distances
is put aside on a vertical axis. Distance between the nearest quasars is put aside on a horizontal axis. The histogram shows that the distances ![]() come across most frequently. Taking into account that
come across most frequently. Taking into account that ![]() m,
m, ![]() m, this distance is equal about 77.4 Mps. It practically is equal to diameter of Universe honeycomb, which is estimated approximately 50-100 megaparsec.
m, this distance is equal about 77.4 Mps. It practically is equal to diameter of Universe honeycomb, which is estimated approximately 50-100 megaparsec.
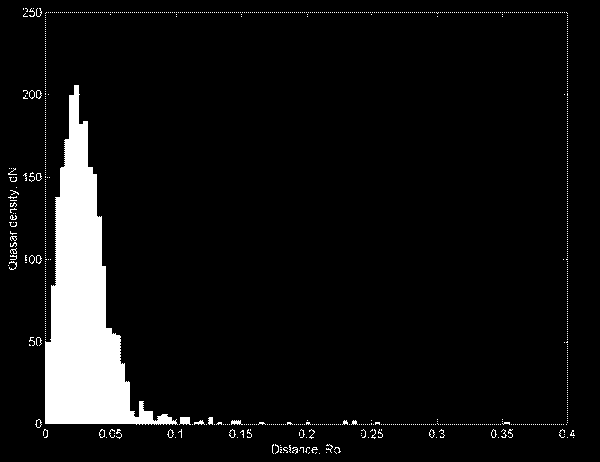
It is obvious, that on the obtained histogram the greatest distances (more than 0.1-0.15 radiuses of gravitational interactions) should generally be excluded from the analysis, as they are interlinked with edge effects, i.e. that the isolated part of the Universe without the taking into account of presence of neighboring quasars was considered.